In the world of foreign exchange (Forex) trading, risk management is the single most critical factor separating consistently profitable traders from those who fail. While many retail traders focus on fixed lot sizes or a fixed percentage of account risk, institutional investors and quantitative funds employ a far more sophisticated methodology: the Volatility Targeting Strategy. This strategy is not about predicting the direction of the market; rather, it is a dynamic approach to position sizing that ensures a consistent level of risk exposure, regardless of the current market volatility. By adjusting the size of a trade based on how much the market is moving, traders can achieve a smoother equity curve and more reliable long-term performance. This comprehensive guide will define the Volatility Targeting Strategy, explain its core mechanics, detail the essential volatility indicators used in its application, and provide a step-by-step framework for integrating this institutional-grade trading strategy into your own Forex operations.
The Problem with Fixed Position Sizing
The traditional approach to risk management involves risking a fixed percentage of one's account (e.g., 1% or 2%) per trade. While simple, this method fails to account for the ever-changing nature of the market.
- Low Volatility: In a quiet market, a fixed-size trade may expose the trader to very little risk, leading to smaller profits and underutilization of capital.
- High Volatility: In a volatile market, the same fixed-size trade exposes the trader to significantly more risk. A wider stop-loss is required to avoid being prematurely stopped out, and the potential for a large loss is dramatically increased.
This inconsistency in risk exposure is the primary flaw that the Volatility Targeting Strategy seeks to correct.
Defining the Volatility Targeting Strategy
Volatility Targeting is a risk management technique where the size of a trade is inversely proportional to the measured market volatility of the asset being traded. The goal is to ensure that the potential loss (the distance from entry to stop-loss) always represents the same dollar amount of risk, regardless of whether the market is calm or turbulent.
The core principle is simple:

By maintaining a constant level of risk, the strategy effectively normalizes the risk contribution of every trade, leading to a more stable and predictable equity curve.
The Mechanics: Position Sizing Formula
The implementation of the Volatility Targeting Strategy relies on a precise calculation that links the desired risk, the measured volatility, and the resulting position size.
The fundamental formula for volatility-adjusted position sizing is:

In practice, the formula is often broken down into the following steps:
Step 1: Define the Target Risk
The trader first determines the maximum dollar amount they are willing to lose on any single trade. This is typically a fixed percentage of the total trading account (e.g., 1% of a $10,000 account is $100).
Account Risk ($) = Account Balance × Risk Percentage
Step 2: Measure Volatility
The next step is to quantify the current market volatility of the currency pair. The most common and effective tool for this is the Average True Range (ATR) indicator.
- ATR: The ATR measures the average range between the high and low of a currency pair over a specified number of periods (e.g., 14 periods). It is expressed in pips or the base currency.
- Stop-Loss Placement: The ATR is used to set a logical, volatility-adjusted stop-loss. A common practice is to set the stop-loss distance at a multiple of the ATR.
Stop Loss Distance (Pips )= ATR × ATR Multiplier
Step 3: Calculate Position Size
The final step is to calculate the position size that ensures the risk from the stop-loss distance equals the defined Account Risk.
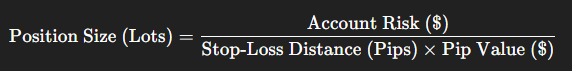
Example:
- Account Balance: $10,000
- Risk Percentage: 1%
- Account Risk: $100
- EUR/USD ATR (14): 50 pips
- Stop-Loss Distance (2 x ATR): 100 pips
- Pip Value (Standard Lot): $10
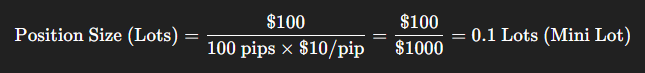
If the ATR suddenly drops to 25 pips (low volatility), the stop-loss distance becomes 50 pips. The new position size would be:
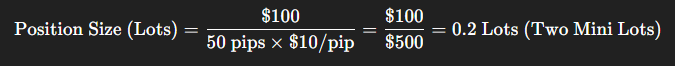
The strategy automatically increases the position size in low market volatility and decreases it in high market volatility, keeping the dollar risk constant.
Key Volatility Indicators for Targeting
While the Average True Range (ATR) is the gold standard for measuring historical volatility and setting the stop-loss, other indicators can be used to confirm the volatility environment.
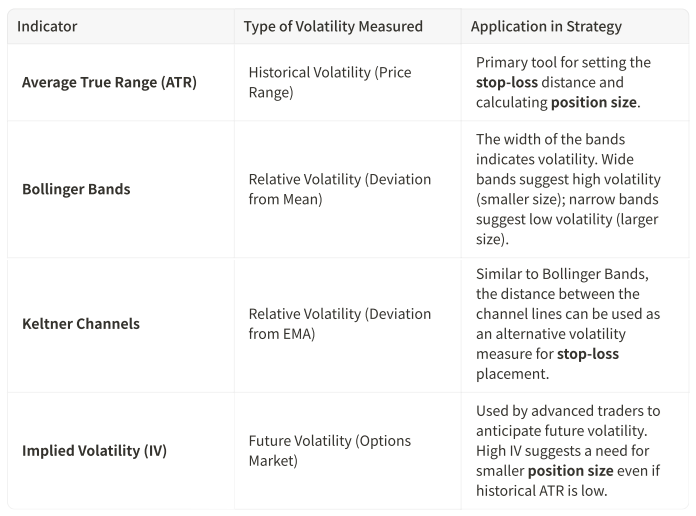
Advantages of Volatility Targeting
The adoption of a Volatility Targeting Strategy offers several profound benefits for the serious Forex trader.
- Consistent Risk Exposure. This is the primary advantage. By ensuring that every trade carries the same dollar risk, the strategy removes the emotional bias associated with large, high-volatility trades and small, low-volatility trades. It allows the trader to focus purely on the quality of the trading signal.
- Smoother Equity Curve. By normalizing risk, the strategy reduces the likelihood of large drawdowns caused by a string of losses during a period of high market volatility. This leads to a smoother, more manageable equity curve, which is a hallmark of professional risk management.
- Optimal Capital Utilization. In periods of low market volatility, the strategy allows the trader to increase their position size without increasing their dollar risk. This ensures that capital is being utilized efficiently, maximizing returns when the market is quiet.
- Adaptive Stop-Loss Placement. The stop-loss is placed based on the current, actual movement of the currency pair (the ATR), rather than an arbitrary number of pips. This makes the stop-loss more logical and less likely to be hit by normal market noise, improving the overall risk/reward ratio.
Integrating Volatility Targeting into a Forex Strategy
The Volatility Targeting Strategy is a risk management framework that can be applied to virtually any Forex trading strategy, whether it is a trend-following system, a mean-reversion strategy, or a breakout strategy.
- Step 1: Strategy Selection. Choose a proven trading strategy (e.g., a moving average crossover system or a support and resistance bounce strategy).
- Step 2: Volatility Measurement. Select the volatility indicator (e.g., ATR 14-period) and the multiplier (e.g., 2.0) to define the stop-loss distance.
- Step 3: Entry Signal and Stop-Loss. When the trading signal is generated, measure the current ATR and calculate the stop-loss distance.
- Step 4: Position Size Calculation. Use the Volatility Targeting formula to calculate the exact position size (in lots) that keeps the dollar risk constant.
- Step 5: Execution and Management. Execute the trade with the calculated position size and the volatility-adjusted stop-loss. The take-profit target can also be set as a multiple of the ATR to maintain a consistent risk/reward ratio across all trades.
Volatility Targeting in Central Banking
The concept of volatility targeting is not limited to trading. It is also a key component of monetary policy for some central banks.
- Inflation Targeting: Many central banks (like the Bank of England or the European Central Bank) practice inflation targeting, which is a form of volatility targeting applied to the rate of inflation. They adjust interest rates to keep the volatility of the inflation rate within a specific, low range.
- Currency Intervention: While less common today, a central bank may intervene in the foreign exchange market to reduce the market volatility of its national currency pair, effectively targeting a lower volatility level to promote economic stability.
Understanding this broader application reinforces the importance of volatility as a primary driver of financial decision-making at both the institutional and governmental levels.
Conclusion: The Professional Edge in Forex
The Volatility Targeting Strategy represents a paradigm shift from simple, fixed-risk models to a dynamic, adaptive approach to risk management. It is the methodology of choice for sophisticated traders and quantitative funds because it addresses the fundamental challenge of trading: the constantly changing nature of market volatility. By using tools like the Average True Range (ATR) to dynamically adjust position size, traders can ensure that every trade contributes the same, controlled amount of risk to the overall trading account. This leads to a more professional, disciplined, and ultimately more consistent Forex trading strategy. In a market defined by its constant flux, the ability to target and control risk through volatility adjustment is the true mark of a professional trader and the key to long-term success in the foreign exchange market.