In the world of Forex trading, moving averages (MAs) are among the most widely used technical indicators. They help traders smooth out price data, identify trends, and generate potential buy or sell signals. Whether you are a beginner learning the basics of technical analysis or an experienced trader refining your strategy, understanding moving averages is essential.
What Is a Moving Average?
A moving average is a statistical calculation that shows the average value of a currency pair’s price over a specific period. Instead of reacting to short-term fluctuations, moving averages filter out market “noise” and provide a clearer picture of the overall price direction.
There are two main types:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Calculates the arithmetic mean of prices over a chosen period.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to market changes.
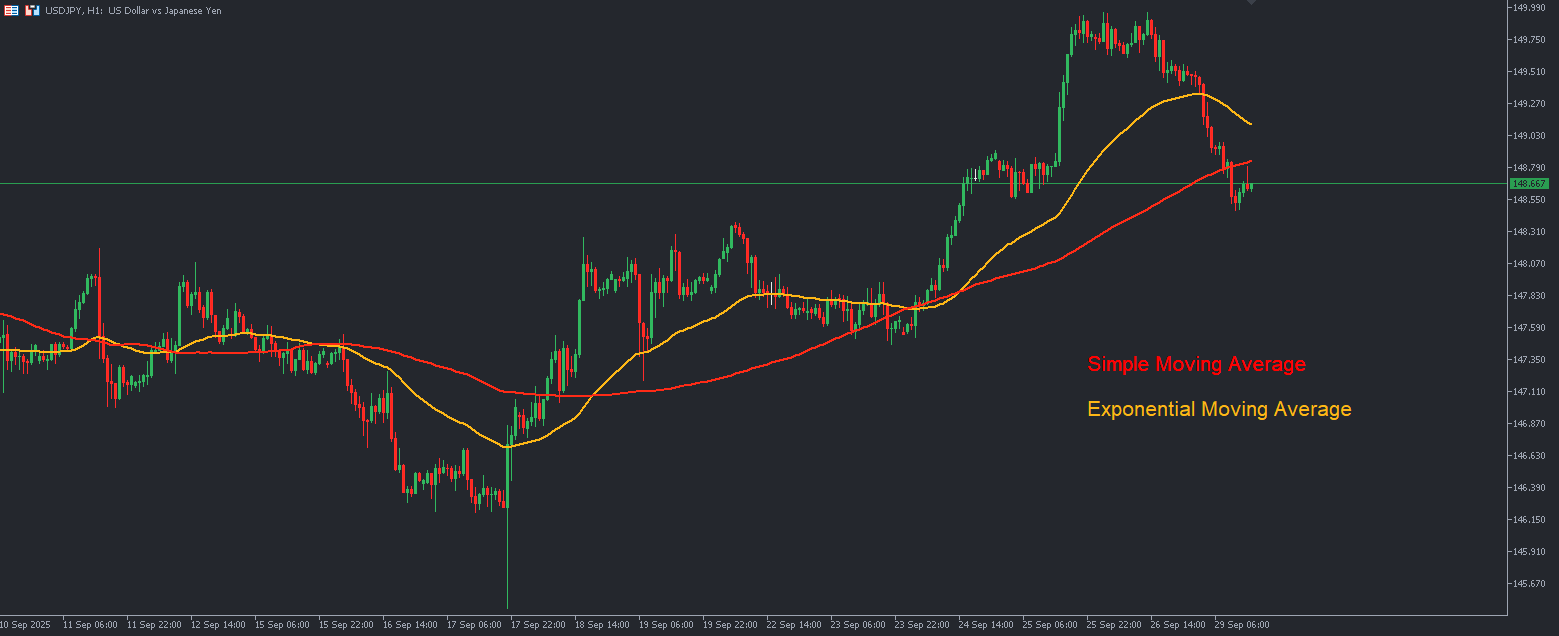
Why Moving Averages Matter in Forex
- Trend Identification: Moving averages help determine whether the market is trending upward, downward, or moving sideways.
- Support and Resistance Levels: They often act as dynamic support or resistance levels where price reacts.
- Entry and Exit Signals: Traders use moving average crossovers or price interactions with MAs to identify opportunities.
- Market Smoothing: MAs filter out volatile price action, allowing traders to focus on the bigger picture.
Popular Moving Average Strategies
- Single Moving Average Strategy: Traders use one MA (e.g., 50-day SMA) to gauge the general trend. If the price remains above the MA, the trend is considered bullish; if below, bearish.
- Moving Average Crossover Strategy: This strategy uses two MAs (commonly a short-term and long-term). A bullish signal occurs when the short-term MA crosses above the long-term MA (“Golden Cross”), while a bearish signal occurs when it crosses below (“Death Cross”).
- Moving Averages with Other Indicators: Many traders combine moving averages with tools like RSI or MACD for confirmation before making trading decisions.
Choosing the Right Moving Average
- Short-Term (10–20 periods): Best for scalpers and day traders looking for quick signals.
- Medium-Term (50 periods): Helps swing traders spot medium-range trends.
- Long-Term (100–200 periods): Used by position traders to analyze broader market direction.
Your choice depends on trading style, time frame, and risk tolerance.
Limitations of Moving Averages
While powerful, moving averages are lagging indicators—they react to price changes rather than predict them. False signals can occur in sideways or choppy markets. To minimize risk, traders often use MAs in combination with other technical and fundamental tools.
Final Thoughts
Moving averages are a cornerstone of Forex technical analysis. They simplify price action, highlight market trends, and provide actionable insights for traders at all levels. However, they should not be used in isolation. A successful Forex strategy involves combining moving averages with other indicators, sound risk management, and a solid understanding of market fundamentals.
By mastering moving averages, traders can improve their ability to identify trends, optimize entry and exit points, and navigate the fast-moving world of Forex trading with greater confidence.
.png)